Wondering if your SEO strategies are working? What about the new strategies everyone is talking about? Should you implement all of them?
Wondering if your SEO strategies are working? What about the new strategies everyone is talking about? Should you implement all of them?
On-Page and Off-Page SEO Explained
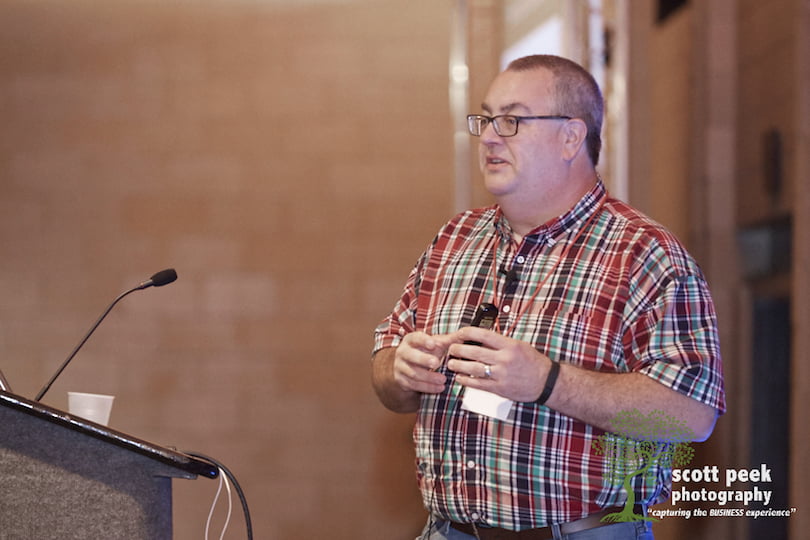
In this presentation at the 2017 Rocks Digital Marketing Conference, Bill Hartzer, Senior SEO Consultant at BillHartzer.com, shares “Everything You Must Know About On-Page and Off-Page SEO.” Bill is founder of DFWSEM Association (2004) and is a US Brand Ambassador for Majestic.com and OnCrawl.com. He has been practicing Organic / Natural SEO since 1996.
Presentation Overview
- Off-Site SEO Linking Basics
- Using Majestic for Link Analysis
- Analyzing and Fixing Your Links
- Using OnCrawl for SEO Analysis
Google has run experiments that excluded links as a factor; Google doesn’t have a way to exclude links yet.
Anchor Text
Anchor text is the underlying text of what people will click on. The way Google used this for ranking a website was very different several years ago. For example, let’s imagine there is text about “red cars” and your page is linked to it. Even if your page is about blue cars, if people were linking to your page using the words “red cars” then you ranked high in Google. This went on for about 10 years, but now things have changed quite a bit. On-page text is just as important as off-page text for SEO.
It’s not just the link, but the link placement. Where the link appears on the page has value. The least valuable place to have a link on a page is in the footer. The higher up on a page a link is, the more likely people are going to see your link and click on it.
Paid vs Natural Links
The actual placement on the page is important. But in the last 10 years, Google has had the technology to understand the difference between a paid link and a natural link – which makes SEO much more difficult. For example, a paid link in the middle of a webpage can be made to look like it is part of the content, but Google knows it is actually a paid link, so they don’t pass “link juice” to that link.
You can have your rank drop due to buying links. Also, the US Federal Trade Commission said that somewhere on your site, sponsored links and ads need to indicate that they are sponsored.
When sites have gotten bad rankings due to links, people have had to comb through the site and examine their links.
Link Schemes Are Bad
Excessive Link Trading – sites where you trade links.
Example: If you have 100 links, but the majority are from trading links, then that’s where you are going to get into some issues. But trading links is not always a bad thing. For instance, a homebuilder website might link to an air conditioning site. If the two sites trade links that could be beneficial. Guest posting can be OK for a few guest posts, but when you get into a certain number, then it could become an issue.
It is very important to get rid of those bad links!
Google Ignores These Types of Links
- “Most” links with “nofollow” link attributes on them
- Most Web 2.0 links
- Google ignores 2nd, 3rd (etc.) link to the same URL on a page
- 1 | 2 | 3 links (the links at the bottom of a page that denote “Page 1”, “Page 2” and so on)
- “Previous” and “Next” links (also referring to pages on a website)
Use Majestic’s link tool to understand your links. Formerly know as Majestic SEO, it has been crawling the web since 2004 and is updated every hour.
When on the Majestic webpage you can put in a search term. We’re using “Rocks Digital” as an example. For Rocks Digital, we would expect certain types of links; however, we would not expect a car shop to link to them. If that kind of link appeared in the results we would want to go in and look at that link.
You can also use Majestic.com for keyword research.
If you put “internet marketing” into Majestic, a lot of these results are based on anchor text and link data, and will be close to what the Google results would be. If the keywords show on Majestic but not on Google, then the website probably has a link problem. You can look at the anchor text and do other keyword research with Majestic.
Aim for high trust flow. You want the trust flow to be high and the citation number to be low. When you look at the two numbers, you want trust flow to be higher than citation. If it’s the other way around, then the site may have a link problem.
A lot of local businesses will have a trust flow number well under 30 or so. With bigger brands, it depends on the industry. B2B companies will have much higher numbers because they will get links from their manufacturers.
If you are linking your website to someone else, then you are passing your trust over to the other website. Your number doesn’t go down because you are linking out. The other site could go down if it is a spam website. Basically, you are going to get links that are linked to you, like one that is linking to all the websites on the web.
Link Maintenance
At certain points in time, I get a spreadsheet of the links to a website, remove the duplicates, and look at the links to see if they are good links or not. From there you can upload to a text file. You then send it to Google or Bing. You can either list the links or give certain domain names, and say that if any link is from a certain domain name then you can have Google or Bing ignore it. If Google looks at your disavow file, you can put your name in there so that Google knows you were the last one to work on that file.
But before you do, make sure you have verified the pages of your website. If you have that disavow file, then you will have people link to different versions. You want to cover all the bases and make sure you disavow all the versions. You upload a text file to Google. With Bing, unfortunately, you have to upload one link at a time.
In the case of a client with 11 million links, thankfully there is a way to upload those links to Bing in an automated process. It saves hours and hours of copying and pasting. In Firefox and Chrome, there are macro actions. You can record that macro, go back and edit it, and have it paste the links for you. Here’s how to disavow links on Bing.
Reminder: You must be logged into Bing’s webmaster tools to use the macro option to upload the links. It really does help a lot.
Disavowing Links on Google
Google will only disavow the links when they have cached the page that is linking to you. If the site is a spam site, it may be 90 days before Google crawls the site. There are ways and services to get Google to go ahead and crawl those sites. Once a page is cached, you can be confident that Google has disavowed that link.
A few reasons you may not be seeing results after disavow:
- It hasn’t been long enough yet
- You disavowed the wrong links
- You disavowed URLs and not domains
- You didn’t upload the disavow file to all versions of site
Identifying New and Lost Links Using Majestic
Compare Tool – you can use this to see how many sites are linking, trust flow, etc.
Keyword Checker – Option or phrase can be done as well.
Analyzing a Site’s Link Profile
- Gather all of the links (Majestic, Google Search Console)
- Review Trust Flow, Citation Flow, Topical and Trust Flow
- Review anchor text, compare vs keyword ranking
Get Links from Trusted Links, Seed Sites
Example: University sites and CNN are good examples of trusted sites. The closer you can get a link to the top of the chain, the better that link will be. Google still looks at page rank (you don’t have the toolbar, but it is still measured).
Trustworthy Domain Info Could Help
- Register your domain for 2+ years (this lets Google know that you care about that domain name)
- Make it public (don’t hide with privacy “whois”)
- Put whois info on your contact page
The domain name should be registered with the actual owner, and not the website designer or web design agency. Case in point: A company has a bad situation with a web designer and wants to leave. If the web designer owns the web name, the client would have to get another domain name.
Untapped Link Sources
- Donate to charity
- HelpAReportOut (HARO) – HelpAReporter.com
- PodcastGuests.com
- Expired Domains
- Blog Aggregators
- Broken Link Building
- Perform Research, Socialize Results
- Find Content with Links and Better Content
For PodcastGuests.com, the podcast is recorded but the podcasters usually promote the podcast themselves (retweet to their followers, etc.). You get a link, you get mentioned.
There is a huge market for expired domain names. Example: Marketingspot.com – Bill bid on the auction, but got in touch with Jay, the former owner, to see if he wanted his former domain back (Bill had been on one of Jay’s former podcasts). The price kept going higher and higher in the auction. Jay decided he was not going to pay thousands of dollars to get his former domain name back.
On-Page Trust Optimization
- Link out to Authority Sites when appropriate
- Privacy Policy, Terms of Service, Disclosure Pages on site
- Bounce Rate, prevent pogo sticking
- Blocked Sites (users can block sites via Chrome browser)
- References and Sources (at end of articles)
- Schema Markup (local sites’ contact matches citations)
There is a fear of linking out, but it is natural to link out. The only question before linking out is whether or not the link will still be valid 6 months from now (example: Wikipedia links are not going to go anywhere).
Another tool Bill recommends is OnCrawl. It does site analysis combining Google Analytics, crawl, and log files.
They will crawl your site, bring in your Google Analytics data, and look at your website’s log files. Looking at your log files you will get the crawl data (how often Google crawls what pages of your website). You can compare that to your Google Analytics data because Google filters out a lot of data.
Example: If you had a website that was redesigned that cannot be accessed from the main page, then they are “orphaned” pages. They are still being accessed by people, but Google is not able to crawl those pages since they are not connected to your main webpage.
Log Analysis – Example: What if the web page designer didn’t put Google Analytics on every page of your site? In that case, you are not going to get the analytics for those pages. OnCrawl helps you to get that information.
There are some pages that are easy to access, while others may take 5 to 6 clicks to get to.
There are 13 places where you can place a keyword in your content on a webpage: meta title, meta description, meta keyword, body text, image alt, anchor link, H1, H2, H3, H4, URL, bold, italic.
What places have the most influence in regards to SEO?
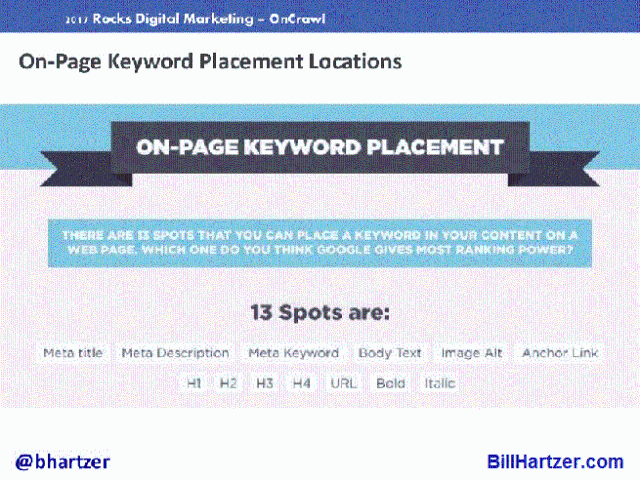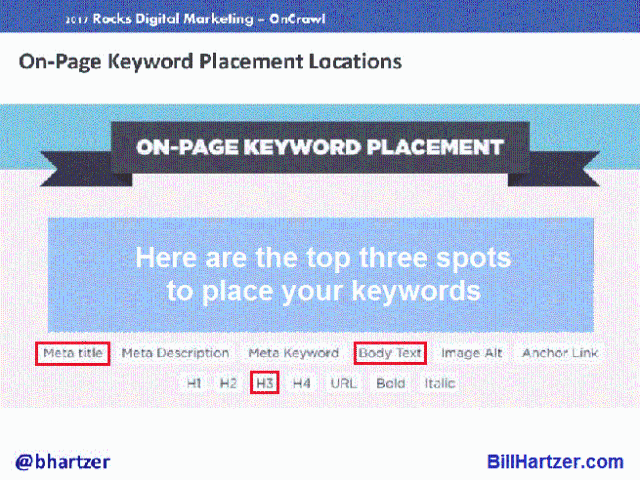
SEO Intelligence Agency – organization that has done hundreds and hundreds of tests. They have determined that the most powerful locations you can put a keyword on a page are:
- Meta Title
- H3 Header Tag
- Body Text
Does Incorrectly Marked-up Structured Data Harm Rankings?
Example: In the area for phone number, you put text. After SEO testing it was found that there was no negative effect on rankings.
Does Page Freshness Affect Ranking?
Example: Changing an old post to the current date. The rank jumped up significantly, but it went back down after 12 hours. Interesting thing is that during the time it jumped up, the sharing of the page increased. As people didn’t share it as much, then the rankings started to go down. On the black hat SEO side of things, there are plugins and programs that every day (or at random intervals) can change the publication date on an article or blog post. Imagine having 100 posts that are refreshed every day. Google, right now, is not analyzing for that, but they may in the future.
If you update images on a post, it will boost up the rankings for 12 hours.
Can you boost link strength by sending traffic to it?
Example: Let’s say Forbes mentions you in an article. Over time, the traffic would go down, but if you did a Google Adwords campaign to send traffic to the Forbes article that links to you, the link strength of the link would go back up.
TIP: You should have the same number of pages on your website as your competitors do – if you want to compete with them. You can increase the value of links to your site if you send traffic to a page that is linking to you.
- A page really needs to be at least 51% unique to get past Google’s duplicate content filter.
- 2–3 internal links = 1 external link of the same value.
Domain Authority Doesn’t Exist
What people see as domain authority is probably the cumulative sum of individual page authority with good internal linking. Also, you can’t get a webpage indexed just with links and anchor text.
Some final SEO testing results – To index a page, you need your target term or an appropriate match on the page. Backlinks with exact anchor text alone won’t get it done.
Does Compressing Images Boost Your Rankings?
No. Testing shows that just compressing an image won’t boost rankings – a page with a larger image stayed in the #1 position.
To view Bill’s slides see below.
Edgar Griggs
Edgar Griggs loves to learn about new technologies and high tech gadgets! You’ll find him at local events around the DFW Metroplex and sometimes blogging for websites like The Interestingly Cool Stuff Blog and his TrendHunter page at TrendHunter.com/CoolTrends!